Introduction to Linear Regression With Python 13 Feb 2019
Using the Auto dataset
Reference: https://vincentarelbundock.github.io/Rdatasets/doc/ISLR/Auto.html
# Common imports
import numpy as np
import os
# Keep a same seed in different executions
np.random.seed(42)
# More common imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sklearn.linear_model
# Directory path of datasets
datapath = os.path.join("datasets", "islr", "")
# Load dataset into a dataframe
auto = pd.read_csv(datapath + "Auto.data.txt", delim_whitespace=True, na_values='?')
auto.head()
| mpg | cylinders | displacement | horsepower | weight | acceleration | year | origin | name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 18.0 | 8 | 307.0 | 130.0 | 3504.0 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 | chevrolet chevelle malibu |
| 1 | 15.0 | 8 | 350.0 | 165.0 | 3693.0 | 11.5 | 70 | 1 | buick skylark 320 |
| 2 | 18.0 | 8 | 318.0 | 150.0 | 3436.0 | 11.0 | 70 | 1 | plymouth satellite |
| 3 | 16.0 | 8 | 304.0 | 150.0 | 3433.0 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 | amc rebel sst |
| 4 | 17.0 | 8 | 302.0 | 140.0 | 3449.0 | 10.5 | 70 | 1 | ford torino |
# Query NaN values
auto[auto.isnull().any(axis=1)]
| mpg | cylinders | displacement | horsepower | weight | acceleration | year | origin | name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 25.0 | 4 | 98.0 | NaN | 2046.0 | 19.0 | 71 | 1 | ford pinto |
| 126 | 21.0 | 6 | 200.0 | NaN | 2875.0 | 17.0 | 74 | 1 | ford maverick |
| 330 | 40.9 | 4 | 85.0 | NaN | 1835.0 | 17.3 | 80 | 2 | renault lecar deluxe |
| 336 | 23.6 | 4 | 140.0 | NaN | 2905.0 | 14.3 | 80 | 1 | ford mustang cobra |
| 354 | 34.5 | 4 | 100.0 | NaN | 2320.0 | 15.8 | 81 | 2 | renault 18i |
# Clean data
auto = auto.dropna()
# Query data types of all columns
auto.dtypes
mpg float64
cylinders int64
displacement float64
horsepower float64
weight float64
acceleration float64
year int64
origin int64
name object
dtype: object
# Select mpg as output(y) and horsepower as one feature(X)
# X and Y become matrix shape
X = np.c_[auto['horsepower']]
y = np.c_[auto['mpg']]
print(X.shape)
print(y.shape)
(392, 1)
(392, 1)
# Plot x vs y by selection two columns of the dataframe
auto.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg')
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x2ae2bfb780>
# Define a linear regression model
model = sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression()
# Fit our linear regression model
model.fit(X,y)
LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None,
normalize=False)
# Make a prediction for 150 horsepower
X_sample = np.array([150]).reshape(1,1) #
print(model.predict(X_sample)) #
[[16.25915102]]
# turn the car model name into index
auto.set_index("name", inplace = True)
auto.head(5)
| mpg | cylinders | displacement | horsepower | weight | acceleration | year | origin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | ||||||||
| chevrolet chevelle malibu | 18.0 | 8 | 307.0 | 130.0 | 3504.0 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 |
| buick skylark 320 | 15.0 | 8 | 350.0 | 165.0 | 3693.0 | 11.5 | 70 | 1 |
| plymouth satellite | 18.0 | 8 | 318.0 | 150.0 | 3436.0 | 11.0 | 70 | 1 |
| amc rebel sst | 16.0 | 8 | 304.0 | 150.0 | 3433.0 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 |
| ford torino | 17.0 | 8 | 302.0 | 140.0 | 3449.0 | 10.5 | 70 | 1 |
# Select our data of interest
data = auto[['horsepower','mpg']]
data.head(3)
| horsepower | mpg | |
|---|---|---|
| name | ||
| chevrolet chevelle malibu | 130.0 | 18.0 |
| buick skylark 320 | 165.0 | 15.0 |
| plymouth satellite | 150.0 | 18.0 |
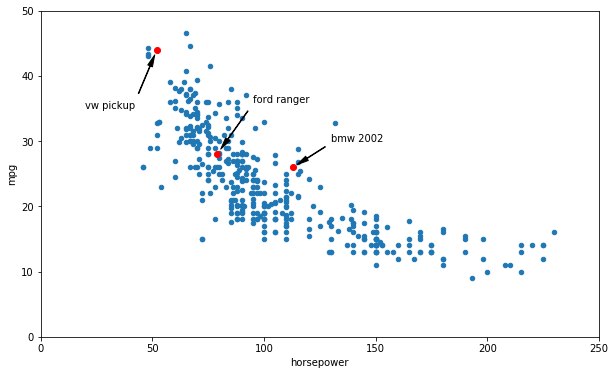
# Show three cases on our plot
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
text_pos = { "vw pickup": (20, 35), "ford ranger": (95, 36), "bmw 2002": (130, 30)}
for carmodel, text_pos_i in text_pos.items():
pos_x, pos_y = data.loc[carmodel]
plt.annotate(carmodel, xy=(pos_x, pos_y), xytext=text_pos_i,
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', width=0.5, shrink=0.1, headwidth=5))
plt.plot(pos_x, pos_y, "ro")
plt.show()
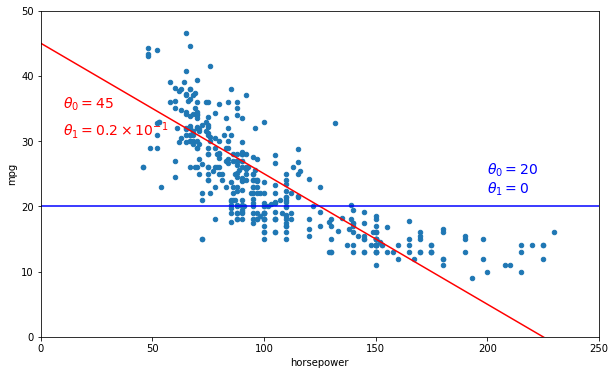
# Plot two hypothesis
import numpy as np
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
X=np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
plt.plot(X, 45 - X/5, "r")
plt.text(10, 35, r"$\theta_0 = 45$", fontsize=14, color="r")
plt.text(10, 31, r"$\theta_1 = 0.2 \times 10^{-1}$", fontsize=14, color="r")
plt.plot(X, 20 + 0 * X, "b")
plt.text(200, 25, r"$\theta_0 = 20$", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.text(200, 22, r"$\theta_1 = 0$", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.show()
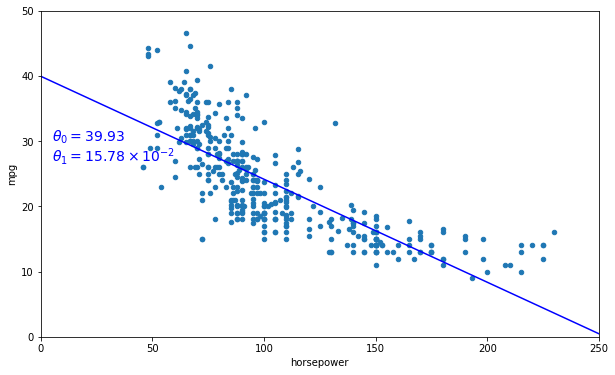
# Obtain one good linear hypothesis
from sklearn import linear_model
linearModel = linear_model.LinearRegression()
X = np.c_[data["horsepower"]]
y = np.c_[data["mpg"]]
linearModel.fit(X, y)
theta0, theta1 = linearModel.intercept_[0], linearModel.coef_[0][0]
theta0, theta1
(39.93586102117047, -0.15784473335365365)
# Plot our estimated good linear hypothesis
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
X=np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
plt.plot(X, theta0 + theta1*X, "b")
plt.text(5, 30, r"$\theta_0 = 39.93 $", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.text(5, 27, r"$\theta_1 = 15.78 \times 10^{-2}$", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.show()
x_test = np.array([150]).reshape(1,1)
y_predited = linearModel.predict(x_test)
y_predited
array([[16.25915102]])
# Draw prediction on our plot
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6), s=1)
X=np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
plt.plot(X, theta0 + theta1*X, "b")
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
plt.text(10, 30, r"$\theta_0 = 39.93 $", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.text(10, 27, r"$\theta_1 = 15.78 \times 10^{-2}$", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.plot([x_test[0,0], x_test[0,0]], [0, y_predited], "r--")
plt.text(150, 20, r"Prediction = 16.26", fontsize=14, color="b")
plt.plot(x_test, y_predited, "ro")
plt.show()
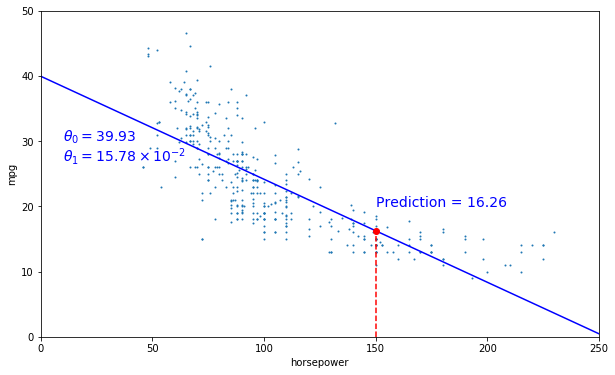
# Separate "nonrepresentative" data points
data_excluded = data[data.horsepower>200]
data_excluded
| horsepower | mpg | |
|---|---|---|
| name | ||
| chevrolet impala | 220.0 | 14.0 |
| plymouth fury iii | 215.0 | 14.0 |
| pontiac catalina | 225.0 | 14.0 |
| buick estate wagon (sw) | 225.0 | 14.0 |
| ford f250 | 215.0 | 10.0 |
| dodge d200 | 210.0 | 11.0 |
| mercury marquis | 208.0 | 11.0 |
| chrysler new yorker brougham | 215.0 | 13.0 |
| buick electra 225 custom | 225.0 | 12.0 |
| pontiac grand prix | 230.0 | 16.0 |
data_excluded[['horsepower', 'mpg']].values
array([[220., 14.],
[215., 14.],
[225., 14.],
[225., 14.],
[215., 10.],
[210., 11.],
[208., 11.],
[215., 13.],
[225., 12.],
[230., 16.]])
# Define data_new without "nonrepresentative" data points
data_new = data[data.horsepower<=200]
data_new.head(5)
| horsepower | mpg | |
|---|---|---|
| name | ||
| chevrolet chevelle malibu | 130.0 | 18.0 |
| buick skylark 320 | 165.0 | 15.0 |
| plymouth satellite | 150.0 | 18.0 |
| amc rebel sst | 150.0 | 16.0 |
| ford torino | 140.0 | 17.0 |
# Compare a full model to a model without "norepresentative" data points
data_new.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
text_pos = { "pontiac catalina": (160, 34), "buick estate wagon (sw)": (140, 37),
"buick electra 225 custom": (160, 30), "pontiac grand prix": (180,40)}
for model, text_pos_i in text_pos.items():
pos_x, pos_y = data_excluded.loc[model]
plt.annotate(model, xy=(pos_x, pos_y), xytext=text_pos_i,
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', width=0.5, shrink=0.1, headwidth=5))
# plt.plot(pos_x, pos_y, "rs")
for xi,yi in data_excluded[['horsepower', 'mpg']].values:
plt.plot(xi, yi, "rs")
X=np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
X_new = np.c_[data_new["horsepower"]]
y_new = np.c_[data_new["mpg"]]
linearModel.fit(X_new, y_new)
theta0, theta1 = linearModel.intercept_[0], linearModel.coef_[0][0]
plt.plot(X, theta0 + theta1*X, "b:", label="Linear model on partial data")
lin_reg_full = linear_model.LinearRegression()
Xfull = np.c_[data["horsepower"]]
yfull = np.c_[data["mpg"]]
lin_reg_full.fit(Xfull, yfull)
theta0full, theta1full = lin_reg_full.intercept_[0], lin_reg_full.coef_[0][0]
X = np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
plt.plot(X, theta0full + theta1full * X, "b", label="Linear model on full data")
plt.legend(loc="lower left")
plt.show()
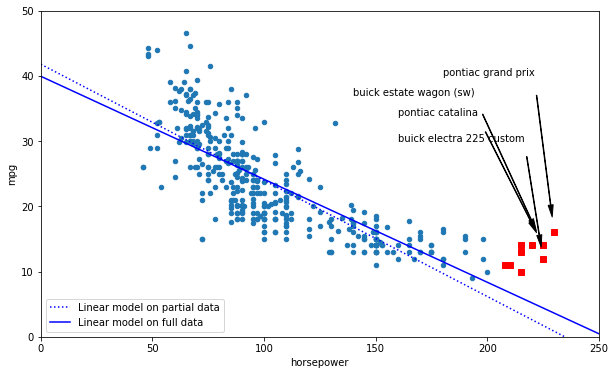
# Fit a polynomial model
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn import pipeline
poly = preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures(degree=4, include_bias=False)
XFullPol = poly.fit_transform(Xfull)
lin_reg2 = linear_model.LinearRegression()
lin_reg2.fit(XFullPol, yfull)
XPol = poly.fit_transform(X[:,np.newaxis])
curve = lin_reg2.predict(XPol)
plt.plot(X, curve)
plt.show()
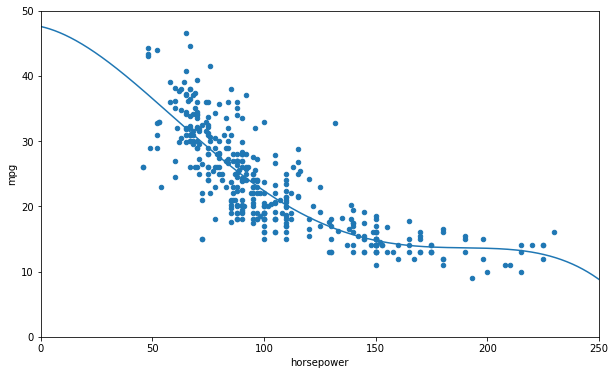
# Fit a polynomial model (Another way)
data.plot(kind='scatter', x="horsepower", y='mpg', figsize=(10,6))
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn import pipeline
poly = preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures(degree=4, include_bias=False)
scaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler()
lin_reg2 = linear_model.LinearRegression()
pipeline_reg = pipeline.Pipeline([('poly', poly), ('scal', scaler), ('lin', lin_reg2)])
pipeline_reg.fit(Xfull, yfull)
curve = pipeline_reg.predict(X[:, np.newaxis])
plt.plot(X, curve)
plt.show()
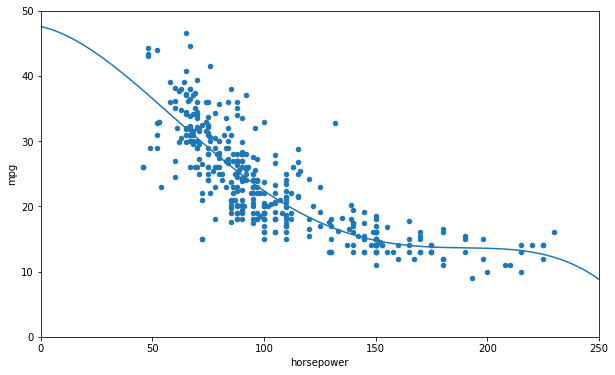
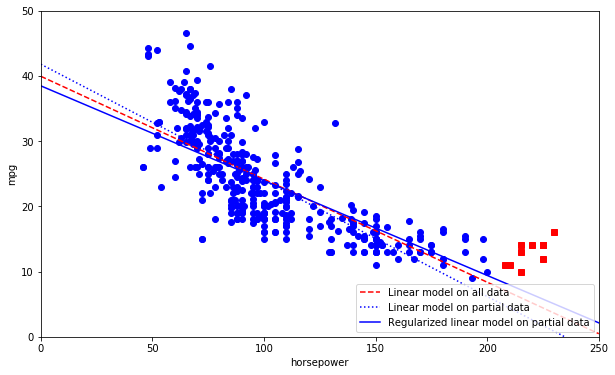
# Add a regularized model and compare this one to the previous models
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.xlabel("horsepower")
plt.ylabel('mpg')
plt.plot(list(data_new["horsepower"]), list(data_new["mpg"]), "bo")
plt.plot(list(data_excluded["horsepower"]), list(data_excluded["mpg"]), "rs")
X = np.linspace(0, 250, 1000)
plt.plot(X, theta0full + theta1full * X, "r--", label="Linear model on all data")
plt.plot(X, theta0 + theta1*X, "b:", label="Linear model on partial data")
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=10**5)
Xsample = np.c_[data_new["horsepower"]]
ysample = np.c_[data_new["mpg"]]
ridge.fit(Xsample, ysample)
theta0ridge, theta1ridge = ridge.intercept_[0], ridge.coef_[0][0]
plt.plot(X, theta0ridge + theta1ridge * X, "b", label="Regularized linear model on partial data")
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.axis([0, 250, 0, 50])
plt.show()
References
Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920052289.do